U3/4-Architecture through history
The origins (1.600.000 – 200.000 B.C)

Australopithecus – The first humanoids to appear in africa. They had no knowledge of fire and did not need shelter.
The new evolved homo erectus, has simple knowledge such as how to obtain fire, and to make a home.
The homes made by the homo erectus are called oval plant huts. Made from Branches, Leaves, Stones and leaves these homes were very simple and basic but met the needs to survive.
These huts were made into a “spring camp” which was made suitable for a group of hunters. 31 of these huts were made in the camp, and 11 were remade every year.
The homes dimensions were 8 to 15 meters long and 4 to 6 meters wide.
Branches were sunk in the ground forming a palisade, then surrounded in stones, and posts to support the structure and main central beam.
100.000 – 40.000 B.C
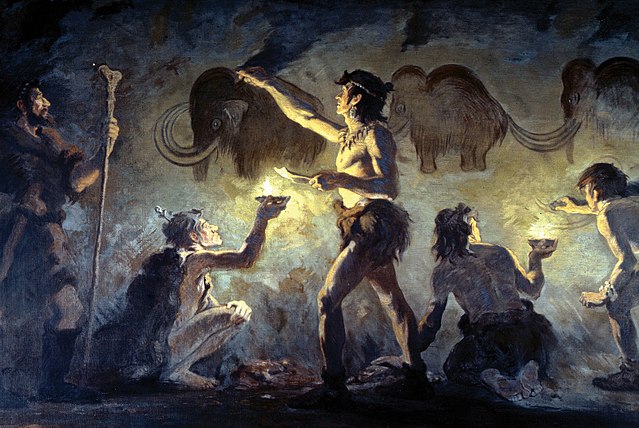
The homo erectus inhabits the caverns of north africa and europe.
They are community orientated, use team work and thinks in symbolic terms.
Things such as flowers being aligned to the sun’s movement were discovered, and the thought and belief of the afterlife shows.
The tombs and burials of old and sick people were found to be more socially complex showing peoples livelihood and wellbeing was valued.

40.000 B.C
Homo sapiens are known to be intellectual and have more skills and ideas.
Paintings, carvings and other such things were found in the caves and shelters, His successor is known as the modern man.
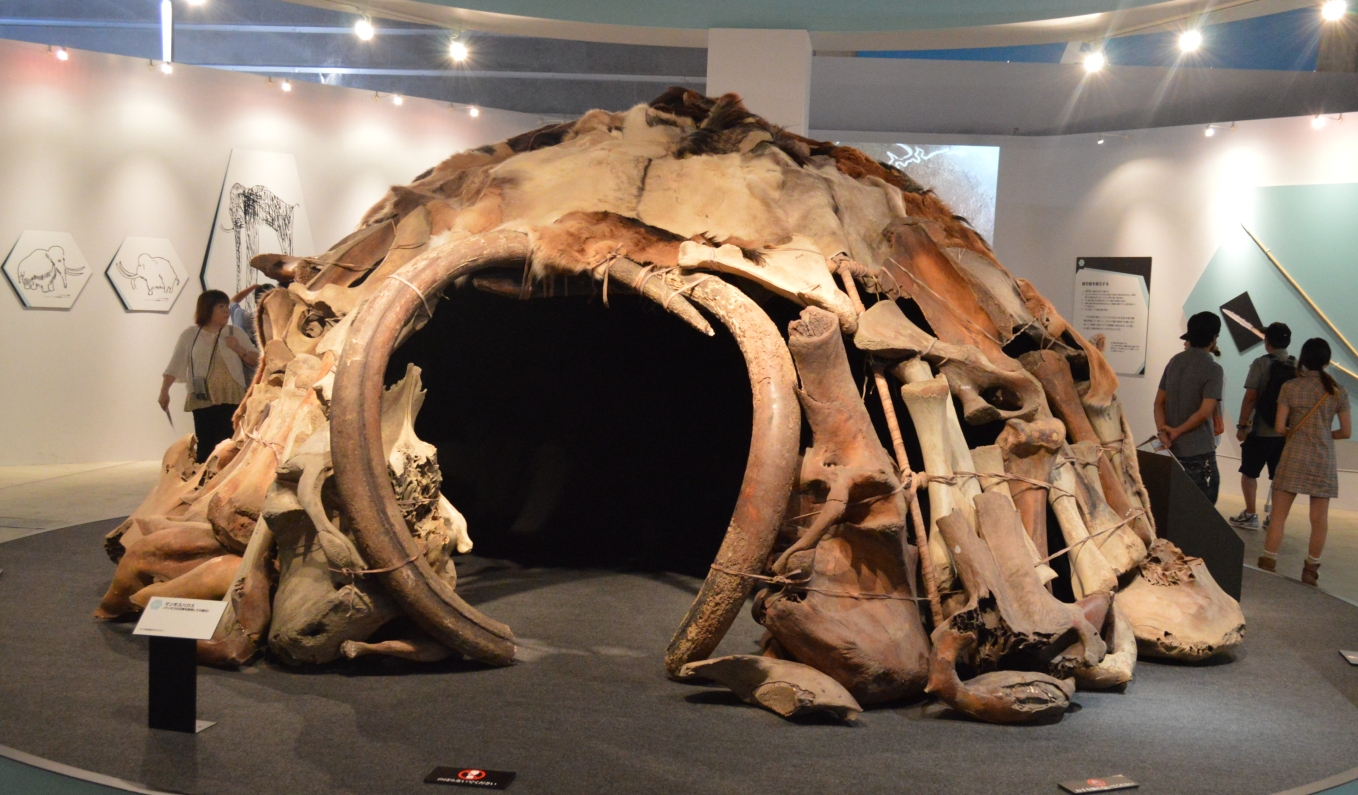
Dwellings and huts were found in eastern europe, circular in shape with a sturdy frame and possible animals skin to cover, these huts show more advances in the living space and practicality.
These are thought to have housed large families and some reached up to 9m in diameter.

8.000 B.C – 100 B.C
Agriculture was firm and encouraged among all the homo sapiens. The construction of more permanent housing was established.
Different types of buildings were discovered perhaps showing the social organization becoming more advanced.
The first great Neolithic city (5.500 B.C) was found which had a capacity of 10.000 Inhabitants.
The transport of natural resources and minerals was found but it was still not an exclusively agricultural community.
The city had defense and security such as a great wall around the perimeter, showing the homo sapiens felt a sense of fear and need to protect their kingdom which they had created.
The houses found were made from pressed adobe bricks with wooden roofs, some of these houses had 2 floors.
There was no such things as front doors, only ladders and holes in the rooves.
Protohistory – There were many Important and large cities found in the valley between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates (Iraq).
Writing and other forms of craft and art is more developed.
/GettyImages-84500182-9d1e12323e0a42dab286dfead4cc31a8.jpg)
The vestiges of these buildings are known as Ziggurats.
Ziggurats had a core of adobe brick and covered in a thick mortar to give it high resistance. These buildings were very advanced and more aesthetically pleasing showing that the architecture had become much more advanced, planned and taken more seriously. These buildings vaguely resemble the pyramids of egypt but instead always housed a mortuary inside. (4000 B.C)
The egyptians – To understand the egyptians and the architecture you need to consider and understand the River Nile.
Egyptian life was peaceful, High quality and survived almost 3000 years.
They strictly followed the cycle of the water and sun. The organization of the temples, cities and such all followed the two perpendicular axes (North-south axis and the east-west axis).
Temples are the most important public building. it was the very center of learning and training of administration.
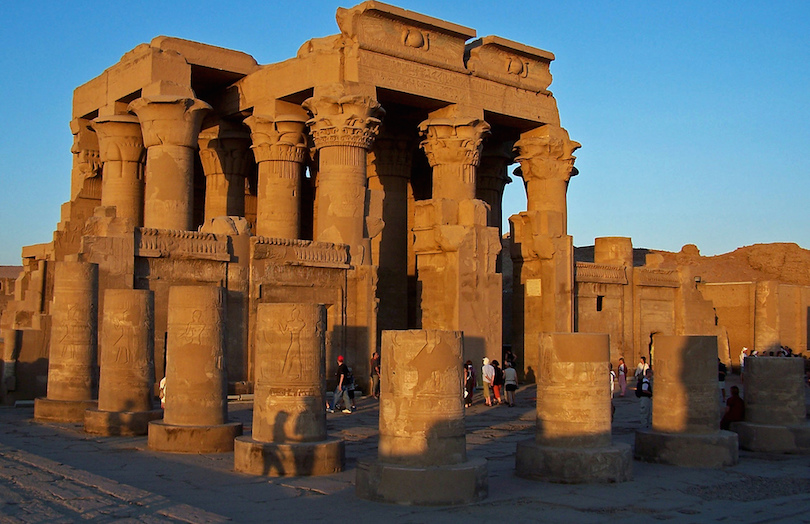

it was seen and known as the house of gods and had a grand entrance usually with surrounding sculptures. Its look and shape stayed the same except for a few subtle changes in its long 2700 years life span.
The temples were a symbol of safety and unbreakability.
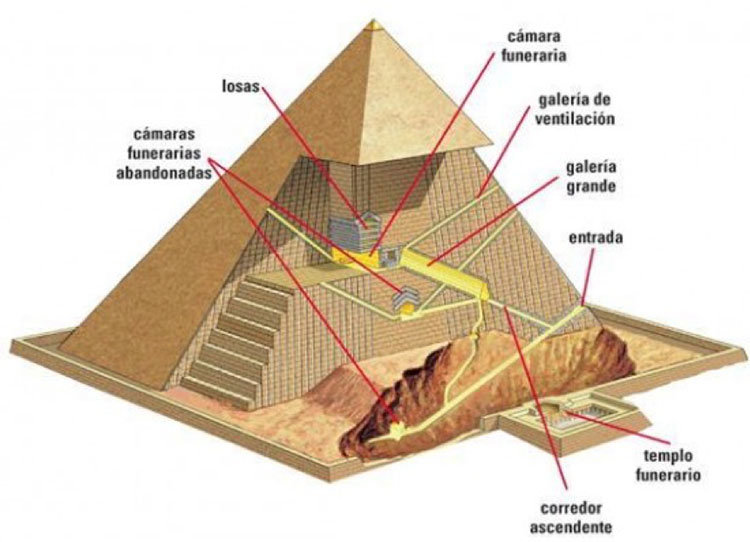
Pyramids – Egyptians were obsessed with life and saw it as too good to end.
The architect Imhoteph made some changes to the architecture such as: replacing the adobe brick and tree trunks with limestone masonry.

(3500 B.C) The Greeks
The Greeks – The greeks learned from egyptian architecture and sculpture and evolved it and created their own art and style of architecture. The architecture shows the equilibrium between the vertical columns and the horizontal ones.
Each aspect of the architecture, the ashlar, columns and sculptures, were carefully worked on and made from the best possible materials. These were not made to show and exhibit wealth but to satisfy the gods and honor the polis.
They were aimed to achieve excellence in every aspect such as detail, execution and aesthetics.
Polis – Cities that grew up around and preached on high ground. They had surrounding farms and encompassed the community’s heart. The center was known as the Agora which was the life of the community.
The temple – known as the most important building , it was dedicated to divinity and was placed on a base or stepped platform. These were large sculptures that had either no, or a very untreated, inside which were not accessible by the public. The facade got a lot of artistic attention as the public rites were celebrated in front of it.
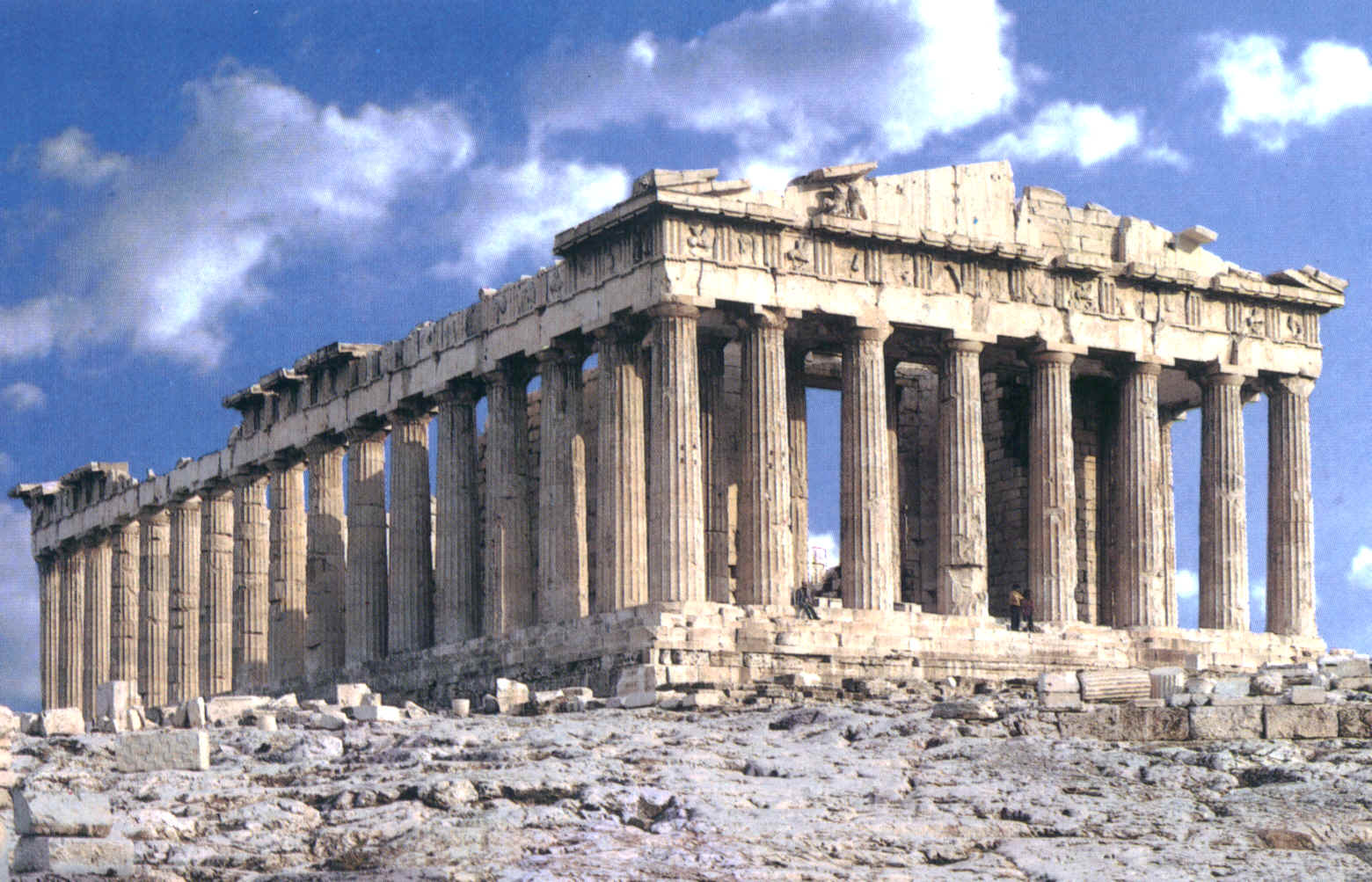

Theater and stadium – These were the largest open air buildings. They were important for the culture, education and community life of the inhabitants. These were not for entertainment however. They had excellent acoustics and great capacity.
Houses – The houses were organized and balanced in contrast to the landscape. They were usually impractical and had little interior space. The were simple and usually only had a small courtyard. The houses were not made from very strong and suitable material and most of the greek houses were left broken down and in bad condition.

(1200 B.C) Romans
Romans – Here the latins settled in the center of the italian peninsula. The romans spread throughout the mediterranean basin and much of europe. The architecture is based the interior closed space but also an exterior space on a grandiose scale. The discovery of concrete allowed the romans to explore and experiment with interior space, lights and shadows. Technical advances such as Arches, vaults and domes were made here (excluding temples). They also did great engineering works such as roads, highways and bridges.
civil works – Sewage networks were made in which some are still used to this day to supply water to cities. Bridges and walls were found here too.

Public buildings – Things such as thermal baths, libraries, schools and a place for commercial relations were found. Other things such a circus was made here which was destined for races, shows and performances.
Some of these public buildings could reach capacities of 45000. These spectators could watch fights between gladiators and beasts or anything in between.

Cities – These were structured with an orthogonal plan in mind. They were usually irregular in shape but later came more organised city blocks. The two main orthogonal streets were: Cardo (North-south) and Decumanus (East-west).
Religious buildings – These buildings followed the greek orders but with more freedom and had modifications. They were more subject to naturalism, vitality, and energy of etruscans. These were usually placed on very high podiums. Temples were also made which were dedicated to all the gods.
The domus and the insulae – Domus: Habitual and home of the richest families. It had a small pond to collect water, with surrounding public relations and private rooms. These had mosaics, paintings and sculptures for decoration. They also had luxuries such as heating installations and drainage. Insulae: The habitual and homes of the plebians who were the main part of the population. These were buildings made up of 3 to 4 floors and made of low quality resources. They had no luxuries other than basic needs such as a bonfire used as cooking and heating.

The Middle ages (A.D onwards)
The roman empire disintegrated and broke down from the overwhelming pressure of the barbarian tribes. The construction of the roman buildings were stopped and made paralyzed from the 5th Century (A.D).
in 410 the Visigoths sacked and stopped following the roman way and moved west to spain and north africa. In 476 the roman empire was finally erased and disappeared.
What was left of the roman empire was taken over and became christianized. Churches and other buildings were now the only important and major buildings and the rest was submerged into anonymity.
The pagan imperial rome’s glory was lost and the christian empire thrived and was established in the east. With this change the pictorial, sculptural and constructive techniques were lost and turned down as well as everything else that didn’t fit or was not justified.
The classic architectural language was developed past the greek and Rome era. and was fully vanished by the 5th and 15th centuries.
